Gynecomastia is the benign enlargement of male breast tissue, typically caused by a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. It can affect one or both breasts and may occur at any age — from newborns and adolescents to older men.
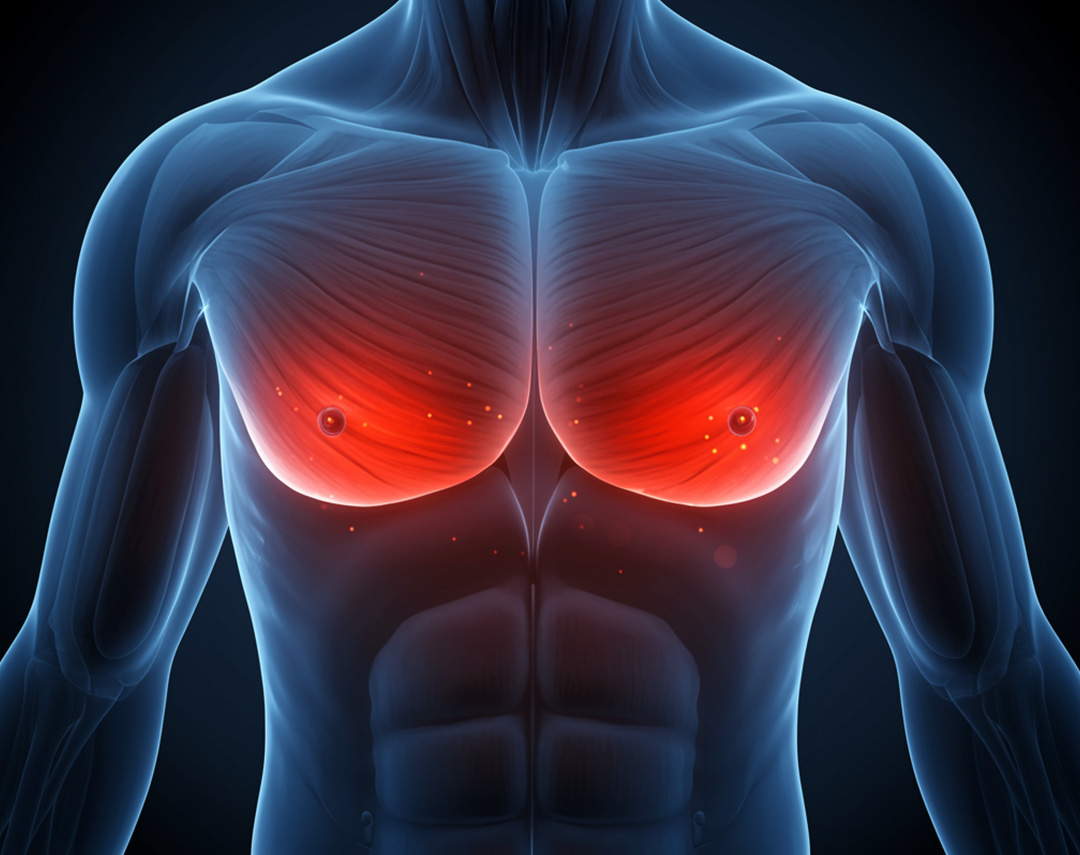
Gynecomastia results when the ratio of estrogen to testosterone shifts, either due to increased estrogen levels, decreased testosterone, or both. Common causes include:
Gynecomastia typically presents as:
It is important to differentiate gynecomastia from pseudogynecomastia, which is fat accumulation without glandular growth, typically seen in overweight or obese individuals.

Diagnosis may involve:
In many cases, no treatment is required, especially in adolescents, as the condition often resolves on its own. Treatment may include:

Comprehensive hormonal evaluations to identify underlying causes

Personalized treatment plans, including medication management and specialist referral

Education and lifestyle counseling to support recovery and confidence
Monitoring for hormonal balance and any recurrence of symptoms
References
